Paper on Fixed-Throughput GRAND with FIFO Scheduling Accepted at ISCAS 2025
The preprint is available on arXiv!
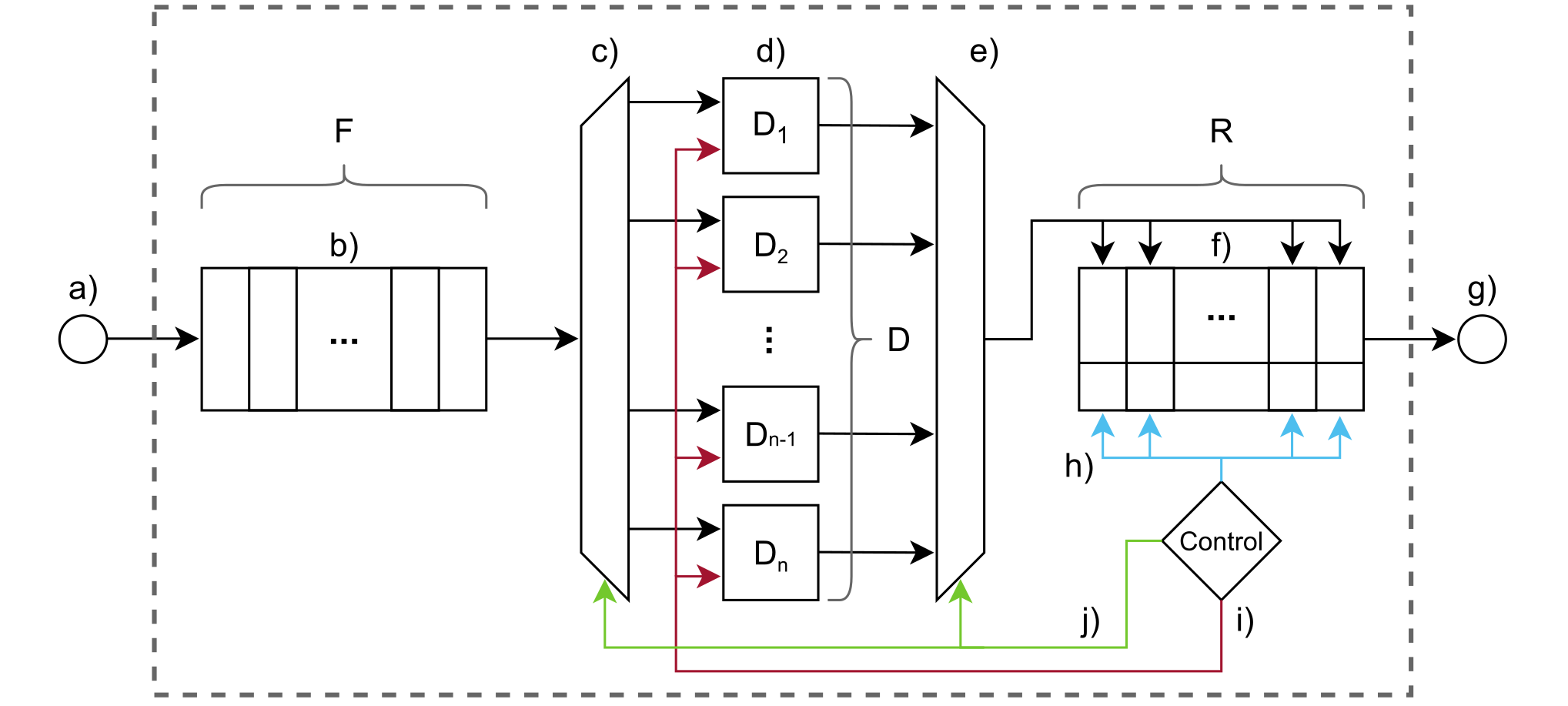
Guessing random additive noise decoding (GRAND) is a code-agnostic decoding method that iteratively guesses the noise pattern affecting the received codeword. The number of noise sequences to test depends on the noise realization. Thus, GRAND exhibits random runtime which results in nondeterministic throughput. However, real-time systems must process the incoming data at a fixed rate in order to avoid losing data. We propose a first-in first-out (FIFO) scheduling architecture that enables fixed throughput while improving the block error rate (BLER) compared to the common approach of imposing a maximum runtime constraint per received codeword. Moreover, we demonstrate that the average throughput metric of GRAND-based hardware implementations typically provided in the literature can be misleading as one needs to operate at approximately one order of magnitude lower throughput to achieve the BLER of an unconstrained decoder.
The paper "Fixed-Throughput GRAND with FIFO Scheduling" is co-authored by Filippo Christen, Darja Nonaca, and Prof. Christoph Studer and will be presented at the International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) in London in May 2025. The preprint is available on external page arXiv.